SCHUHFRIED specific terms
|
Term |
Description |
Synonyms and related terms |
|---|---|---|
|
Vienna Test System |
The Vienna Test System is SCHUHFRIED's core product for digital psychological assessment. It allows administering and scoring our tests in many different languages. Testing can be flexibly adapted to the respective use case. There are options for unsupervised and supervised testing or for group testing. The Vienna Test System is available in two product versions, VTS online and VTS offline. |
VTS, VTS Online, VTS Offline, VTS basic software, VTS administration software |
|
VTS online |
VTS online is a modern, browser-based version of the VTS. All you need to use VTS online is internet access. Your data is secured in our cloud-based infrastructure. Further information on the differences between VTS online and VTS offline can be found here. |
Portal, VTS Portal, VTS basic software, VTS administration software |
|
VTS offline |
VTS offline is a software package that allows you to install VTS on the devices of your choice. VTS can be installed and configured on a single device (single workstation installation) or on a server for use in a local network (server/client installation). VTS offline is the on-premise solution from SCHUHFRIED. |
VTS basic software, VTS administration software |
|
VTS Admin Client |
The VTS Admin Client is the VTS administration software installed on the desktop, which can be used to manage settings, users, tests, and test results. The VTS Admin Client is a function of VTS offline. In VTS online, all functions of the VTS administration software can be managed and executed directly in the browser. Since VTS version 8.28, the user interface of VTS online is also the standard user interface of the VTS Admin Client. This means that VTS offline and VTS online look identical. Further information on the differences between VTS online and VTS offline can be found here. |
AC, Admin console, VTS basic software, Admin Client, VTS administration software |
|
VTS Testplayer |
The VTS Testplayer is an application that runs the tests and is opened from the VTS administration software as soon as a test is started. For many tests, the testplayer can be started directly in the browser (= Testplayer Web). For specific tests, especially those that require an additional input device, it is necessary to administer tests via a locally installed application (= Testplayer Client). Whether testing is carried out in the browser can be specified in the VTS settings. |
|
|
Testplayer Web |
The Testplayer Web is the modern browser-based version of the VTS Testplayer. |
VTS Testplayer |
|
Testplayer Client |
The Testplayer Client is the version of the VTS Testplayer that can be installed locally. The Testplayer Client must be installed on the device on which the testing is to be administered. This version of the Testplayer is required if time-critical tests are administered that require additional input devices such as the Response Panel. |
VTS Testplayer |
|
Marketplace |
The Marketplace is the online information and purchasing platform (webshop) for SCHUHFRIED products such as test licenses, input and output devices, administration software. |
|
|
VTS basic software |
This refers to the VTS administration software, which is required for the managing persons, test results, and settings. The testing is configured and started in the VTS administration software (= VTS basic software). A separate license is required to use the basic software. Additional licenses are required for test administration and certain functions. |
VTS, VTS online, VTS offline, VTS administration software |
|
Licenses |
The VTS administration software as well as certain features, such as the ranking module and all our tests, require licenses in order to be used. Test licenses can be purchased as single test licenses (pre-purchased number of test administrations without an expiration date) or annual licenses (flat rate for a specific period). |
|
|
SCHUHFRIED Selection |
The SCHUHFRIED Selection (SFS) refers to a selection of SCHUHFRIED tests that can be used to answer many psychological assessment questions with minimal administrative effort. One SCHUHFRIED Selection license is used per test session, regardless of the number of tests in the given test sequence. The only requirement is that the given tests are part of the SCHUHFRIED Selection. Additional tests thar are not part of the SCHUHFRIED Selection can be added to the test sequence, provided that the corresponding licenses have been purchased in advance. The tests in the SCHUHFRIED Selection also form the basis for the Test Assistant. |
SFS |
|
Test Generator |
The Test Generator (TG) is a tool in the VTS that allows you to create your own questionnaires, surveys, knowledge tests, or simple performance tests in just a few steps. The Test Generator is available to everyone who works with the VTS. Either TQ or SFS licenses are required to administer and score the tests you create. |
TG |
|
Analytics |
Analytics is a function in VTS online that allows you to further analyze the results of your test takers. For example, you can compare the number of tests in specific time periods, the distribution of test scores (also for specific subgroups), and the test results of individuals, and evaluate them over several test dates. |
VTS Analytics |
|
Test Assistant |
The Test Assistant is a feature in VTS online that helps you quickly and easily find the recommended test selection for your specific question. Simply enter the search term, e.g., pilot, train driver, sales representative, manager, in the search field. The search result provides you with the test sequence recommended by SCHUHFRIED, which can be specified (or customized) directly in the VTS. A cross-test evaluation (see BATEVA) is also provided for the recommended test sequence. |
|
|
Extended Options |
The Extended Options refer to the settings that can be accessed in the Testing tab by clicking the Configure button ( |
|
|
Direct Testing |
Direct Testing is a SCHUHFRIED-specific term used for tests that are not started from the VTS administration software, but directly via the Testplayer. The Testplayer is first started as a separate application at the test station (when using the Testplayer Client) or opened directly in the browser (when using the Testplayer Web). The test taker can then directly log in and start the test. Depending on the setting selected in the VTS, the test taker logs in either by entering a personal ID (assigned by the test administrator to the persons already created in the VTS) or by entering their personal data themselves. Direct Testing is particularly relevant for group testing on site, as it allows multiple tests to be prepared and test takers to start their their tests at the same time. |
|
|
Online Testing |
Online testing refers to the administration of tests in a browser. The test taker can therefore take the test at any location, provided that a stable internet connection to the VTS is available (and the conditions on site allow testing). |
Open Mode, Proctored Mode, Online Testing, Web Testing, Invite, Invite links |
|
Demo Account |
A demo account provides the opportunity to explore VTS online free of charge. It includes most functions and demo versions of 10 tests from the SCHUHFRIED Selection. When a test is started in demo mode, only instructions and practice items are shown, but the test items are not included. To set up a demo account, go to VTS online and register for free using the Register for demo account button. |
|
|
Single Workstation |
A single workstation (single workstation installation) refers to a local installation of the VTS offline on one PC. The Admin Client, the Testplayer and the database are located on the same device. Only testing in controlled mode is possible. |
Single workstation installation |
|
Server Setup |
A server setup refers to an installation of the VTS offline on a central server. The database and the VTS administration software are located directly on the server. Admin Clients and Testplayer Clients can be installed on other devices within the same network. This allows users to access a centrally hosted VTS from other locations. This can reduce maintenance costs. All locations use the same database. However, it is possible to make only certain parts of the database visible to one user, see Multi-client. |
Server setup, server-client system |
|
Multi-client |
If a server is used to host the VTS for multiple locations, departments, etc. that should not have access to each other's personal data and test results, multi-clients can be created. Users in a multi-client only have access to the relevant part of the database, i.e. only to personal data, test results, and test licenses that were created via this multi-client. |
Mandant |
|
Environment |
We primarily refer to environments in the context of VTS online. Each organization or user receives their own environment in VTS online. An environment contains the data of test takers, their results, test licenses, and the configured settings. |
|
|
Test Services |
Test Services include all services provided by SCHUHFRIED that aim to develop customer-specific adaptations or solutions. These include, for example, advice on the use of the VTS (test selection), the creation of customer-specific scorings, or the development of new or customer-specific tests or test content (such as customer-specific norms). |
|
Hardware
|
Term |
Description |
Synonyms and related terms |
|---|---|---|
|
Input and output devices |
All devices that are required for operating and administering specific tests. These include devices for response input (e.g., the Response Panel), as well as devices for presenting stimuli, such as the Peripheral Perception-R device. An overview can be found here. |
Peripheral devices, Hardware |
|
Hardware |
All available peripheral devices. |
Peripheriegeräte, Ein- und Ausgabegeräte |
|
Response Panel |
A device for recording motor inputs with millisecond precision, e.g., via color keys, joysticks, or control knobs. It measures, for example, reaction time (RT), two-hand coordination (2HAND), or the ability to react (DT). There are two versions: the Response Panel Advanced (Ag) with keys and control knobs and the Response Panel Universal (Ug) with keys, control knobs and joysticks. |
Panel |
|
Peripheral Perception Unit 2 |
A device (PP-HW2) and test (PP-R) for assessing peripheral perception, i.e., the reception and processing of stimuli outside the focused (central) field of vision. While the test taker performs a concentration task on a PC screen (a test called PP-R in the VTS), critical stimuli are generated at intervals on the laterally positioned sensor bars (part of the PP-HW2 hardware), to which the test taker must react as quickly as possible. PP-R is particularly relevant for testing in a traffic context, but also in sports. |
PP-R, PP-HW2 |
|
Motor Performance Series |
A device (MLS work panel) and test (MLS) for assessment of fine motor abilities by static and dynamic items for finger-, hand- and arm movements, e. g. tapping or the tracking of a path. |
MLS |
Testing
|
Term |
Description |
Synonyms and related terms |
|---|---|---|
|
Adaptive testing |
In contrast to traditional linear testing, where each test taker is given the same items, adaptive testing uses an algorithm that adjusts the difficulty of the items based on the performance shown so far. The items are drawn from a large pool of items. This allows for very accurate measurement at all ability levels with reduced test duration. The disadvantage may be that the test duration varies more between test takers and that the tests are perceived as difficult (lower test acceptance). |
computerized adaptive testing (CAT) |
|
Linear testing |
In contrast to adaptive testing, where the items are adapted to individual performance, in linear testing all test takers are given the same items in the same order and with increasing difficulty. The advantage is a more predictable test duration and a more pleasant testing experience (higher test acceptance) for the test taker. However, the test duration tends to be longer than with adaptive testing, and floor and ceiling effects are more likely to occur (i.e., the difficulty of the test does not match the ability of the test takers). |
|
|
Randomized testing |
Similar to linear testing, in randomized testing, the items are given in ascending order of difficulty. The average difficulty and the distribution of item difficulty are comparable for all test takers. However, the specific item content differs between test takers, as items are drawn randomly from a large pool of items. The advantage of randomized testing is that all test takers work on the same number of items, but are given different items. |
|
|
Test acceptance |
Test acceptance refers to the extent to which test takers are willing and motivated to participate in a psychological test and perceive it as fair and meaningful. It reflects how well a test meets the needs and expectations of the test taker in terms of comprehensibility, relevance, duration, design, and difficulty. High test acceptance generally leads to a lower dropout rate and more reliable, valid test results, as test takers actively participate in the test and are more committed to working the test. |
|
|
Test battery |
A test battery refers to several tests that are saved and given in a predefined order without interrupting the testing process. In VTS, every user can create and store any number of test batteries created with licensed tests. |
|
|
Test modes |
While traditional paper-and-pencil tests must necessarily be administered on site and under supervision (controlled mode), many digital tests also allow sending a test link so that the test taker can complete the test independently (open mode) or be supervised online (proctored mode) – in other words, different test modes are available. The test mode in which a test can be administered depends not only on the technology on which it is based, but also on other factors such as the current legal situation regarding assessment, the test design, or the consent of the test authors to use the test for certain test modes. The Marketplace shows which test modes are supported for each test: 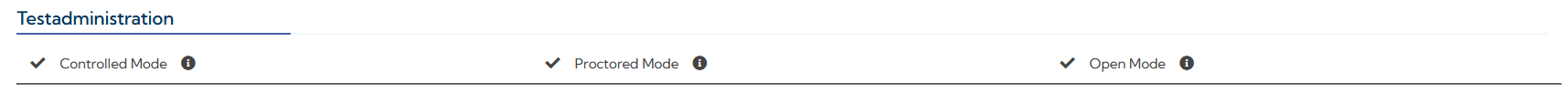
In the VTS, you can filter your licensed tests by the available modes on the Testing page: 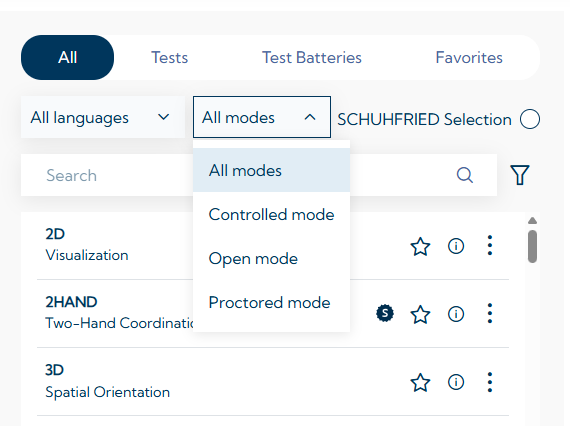
|
|
|
Controlled mode |
Controlled mode refers to the administration of a test on site and under the supervision of a trained test administrator. This allows any questions or uncertainties on the part of the test taker to be clarified quickly. This mode also offers the highest level of test security, as cheating can usually be ruled out. Tests that require special input devices such as a Response Panel are only available in controlled mode. |
|
|
Open mode |
Open mode refers to the unsupervised administration of a test via a test link generated by the VTS and usually sent by email. Test takers are therefore free to decide how and when they want to take the test. For test administrators, this means minimal administrative effort and maximum reach, but test security is lower. |
Online testing |
|
Test link |
The VTS offers the option of creating links that can be opened by the test taker in a standard browser to start an online test in open or proctored mode. The links can be sent directly from the VTS to the test taker by email (“Invite” button) or to the test administrator (“Proctoring” button): 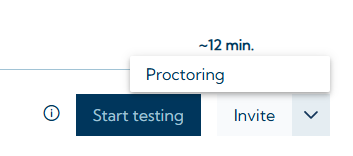
|
Invitation link, invite |
|
Proctored mode |
Proctored mode refers to the supervised administration of a test via a test link. This link is generated via the VTS and sent directly to the test administrator (proctor). The test taker usually receives the link by email or via an online tool shortly before the agreed test date. Proctored mode combines the advantages of open and controlled mode (location-independent but supervised testing), but requires increased administrative effort, as appointments must be coordinated and technical infrastructure and a test administrator must be available for supervision. As with controlled mode, several people can be supervised simultaneously via proctoring if the technical facilities are available. This means that group testing (up to a certain number of people) is also possible in proctored mode. |
Online testing, proctoring |
|
Test administrator |
(Trained) person who supervises a test to prevent cheating and answer questions, and ensures that the test is completed in accordance with the instructions (= the test taker understands how to work the test). The test administrator usually supervises the testing on site, but can also supervise online testing via a meeting tool (“proctored mode”). |
Proctor |
|
Test administrator window |
The VTS test administrator window allows the test administrator to intervene during testing at any time. This is only possible during supervised testing, as the test administrator must enter a key combination directly on the keyboard. You can find out which keys to press when you start a test under Notes on the test administration: 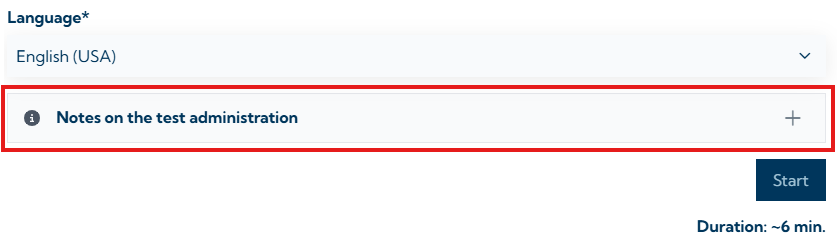
Intervention may be necessary in various situations, such as technical problems, questions from the test taker, or if too many errors occur during the practice phase. In these cases, the test administrator has various options available:
The test administrator window can be password protected to prevent test takers from accessing it during testing. |
|
|
Test administrator notice |
If the test taker makes too many mistakes during the practice phase, this message is displayed: 
In this case, the test administrator must decide via the test administrator window how to continue or abort the test. Whether such a message is displayed depends on the test. |
Red Window |
|
Test taker |
Person who is working on a test. Depending on the application, test takers can be clients, patients, applicants, employees, athletes, etc. |
|
|
Test station |
Workstation where testing takes place. For a single workstation, this is the PC on which the VTS is installed. For a server setup, this is all PCs in the network on which the Testplayer is installed and where testing can be started. With VTS online, the test station can be any (internet-enabled) device on which testing can be started. |
|
|
Test security |
Test security means that test materials and procedures are protected in such a way that the results obtained reflect only the psychological constructs measured – and not the test participants' knowledge of the test content. This includes protecting test items, scoring keys, and interpretation algorithms from unauthorized access or reproduction, as well as conducting tests under controlled conditions, for example in test centers or using secure, encrypted IT systems. |
|
Scoring
|
Term |
Description |
Synonyms and related terms |
|---|---|---|
|
Norm |
A norm is a comparison group with which the test results of a test taker are compared. The comparison group represents a population with regard to certain relevant characteristics. As standard, we offer at least one representative norm sample for the entire population of the DACH region for our tests. The people in this norm are therefore distributed in terms of age, gender, and, in some cases, educational level in the same way as the entire population of the DACH region. |
Norm sample |
|
Convenience sample |
In contrast to a representative norm (sample), individuals are tested ad hoc for a convenience sample. This means that no specific sociodemographic characteristics are taken into account when selecting test takers. Of course, norms for tests can also be created from convenience samples, but when interpreting or using such norms, their suitability for the respective question must be checked. |
|
|
Norm-referenced score |
A norm-referenced score allows the performance of a test taker in a test to be compared with the performance of a comparison sample (norm sample). Norm-referenced scores should usually be used for the objective interpretation of test results. The most common norm-referenced scores are percentile ranks (PR), T scores, Z scores, and IQ scores. |
|
|
Percentile rank |
A percentile rank is a statistical value that relates the test result of a test taker to the selected comparison group (norm-referenced score). The percentile rank indicates the percentage of the comparison group that achieved a lower or equally good result, e.g., PR = 80 means that 80% of the comparison group achieved a worse or equally good result and only 20% achieved a better result. |
PR |
|
Raw score |
Term for the number of points or individual items solved (score or total score) that were determined for a person in a specific test. This value is considered “raw” because it does not represent performance in comparison to a reference population. Raw scores are therefore transformed into norm-referenced scores for interpretation. |
Score, total value, scale value |
|
Person parameters
|
If a test is based on an IRT model (modern test theory or item response theory), a person parameter is determined based on the test taker's response pattern and the item parameters (e.g., item difficulty) of the items completed. This represents the raw score of the test with positive scores indicating a higher ability or stronger expression of the trait measured. |
Performance parameter, theta |
|
Confidence interval |
A confidence interval is the range around an estimated parameter (e.g., person parameter) that indicates the range in which the true value lies with a certain probability (confidence level, e.g., 95%). The size of the confidence interval is determined by the standard error of measurement or the reliability of the test. |
CI, confidence interval |
|
Standard norm |
Standard norms are primarily calculated by linear transformation of normally distributed raw scores. Unlike norms derived from area transformation (percentile ranks), they are therefore not distribution-free. However, percentile rank norms are often generated first by area transformation and then assigned standard norms (from a table). This means that even if standard norms are available, it cannot necessarily be assumed that the raw scores are normally distributed. |
PR |
|
Floor and ceiling effects |
If a test exhibits floor effects, it means that it cannot differentiate well between individuals at the lower end of the performance scale. In a math test, for example, test takers who cannot do math at all would receive the same norm-referenced score as those who perform below average in mathematics. At the lower end of the ability distribution (the test floor), it would therefore not be possible to make any differentiated statements about the performance of a test taker. Ceiling effects mean the same thing, only at the upper end of the performance scale. |
|
|
Profiling |
Profiling is used to check whether a person meets a previously defined requirement. To do this, a target profile for the minimum requirement and an ideal profile are created. A comparison of a person's test results with the ideal profile yields a so-called fit score, which indicates how well or poorly a person meets the requirement. The score ranges from 0 (the person does not meet the requirement) to 1000 (the person perfectly meets the requirement). If a test result falls outside the target profile, the person does not meet the requirement. |
Fit score |
|
Ranking module |
The ranking module is a licensed feature in the Vienna Test System (only available in the VTS Admin Client) that allows the test results (from multiple tests) of several people to be compared. The results of each person are compared with a previously defined ideal profile to calculate a so-called fit score. Based on this fit score, the persons can then be automatically ranked from the person who best matches the ideal profile to the person who least matches the profile. Within the ideal profile, a target range for the minimum requirements can also be defined – if a result falls outside this target range, the person is listed in a separate ranking. Unlike ideal profiles, which are created by us in BATEVA and therefore cannot be changed by customers without consulting us, ideal profiles can be defined and adapted in the Vienna Test System using the ranking module. However, we are also happy to advise you on their creation. |
Ranking module |
|
BATEVA |
A BATEVA (= Test battery evaluation) is an evaluation of multiple tests (test battery) on one page, tailored to the individual needs of the customer. The customer can decide which variables are displayed, how they are named and arranged. A traffic light can also be implemented for each variable to make the overview even easier. A BATEVA usually consists of the results table and the profile. Fit scores can also be calculated and displayed in the table. The ideal and target ranges of the fit scores can be displayed in the profile using green and red areas. A BATEVA can be created specifically for individual customers according to their requirements and can also be flexibly adapted. |
|
|
Fit score |
The fit score describes how well a person's test results match a previously defined ideal profile, usually a job requirement profile. The fit scores used by SCHUHFRIED range from 0 (lowest match between test results and ideal profile) to 1000 (perfect match between test results and ideal profile). The fit score, is calculated based on the deviation of the test results from this ideal profile. In addition, all variables contained in the ideal profile can be weighted individually. Fit scores can either be configured in the ranking module itself or programmed as part of a BATEVA. |
FIT Score |
|
Word report |
A word report is a verbalized feedback of the test results. The customer-specific version offers the option of focusing on exactly those results that are most relevant to the customer. This means that test results can also be interpreted by trained individuals without psychological training. Word reports can be designed according to customer requirements, including being designed in the customer's corporate identity. Word reports can be created either by the users of the VTS themselves (Settings → Word report templates) or by SCHUHFRIED. The Word report can be created for a test as well as for a test battery. |
|
|
Premium Report |
Premium Report refers to verbal results reports tailored to specific job profiles, e.g., for management, sales, staff. The general advantage is that everything is extracted from the simple numerical test results. Testing is resource-intensive, so test results should be used as comprehensively as possible. This is possible with reports that contextualize test results and use them for interviews, onboarding, and training suggestions. Premium Reports require seperate licenses; and each report generation consumes one license. |
|